|
I am a fourth-year Ph.D. student @ Computer Science in Wu Wenjun Honorable Class, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU) & Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, advised by Prof. Cewu Lu. Previously, I got my B. Eng. degree @ Computer Science and Engineering, and B. Ec. degree @ Finance from SJTU in 2022.
|

Photo @ İstanbul, Türkiye
|
|
[Aug. 2025] AirExo-2 is accepted by CoRL 2025. See you in Seoul! |
|
Representative papers are highlighted. * denotes equal contribution. † denotes corresponding author(s). |
|
Jingjing Chen*, Hongjie Fang*, Chenxi Wang, Shiquan Wang†, Cewu Lu† arXiv, 2025 paper / code / project page Propose an object-centric history representation based on point tracking, which abstracts past observations into a compact and structured form that retains only essential task-relevant information. Tracked points are encoded and aggregated at the object level, yielding a compact history representation that can be seamlessly integrated into various visuomotor policies. Our design provides full history-awareness with high computational efficiency, leading to improved overall task performance and decision accuracy. Our history-aware policies consistently outperforms both Markovian baselines and prior history-based approaches. |
|
|
Ying Feng*, Hongjie Fang*, Yinong He*, Jingjing Chen, Chenxi Wang, Zihao He, Ruonan Liu, Cewu Lu† arXiv, 2025 paper / code comming soon / project page Propose DQ-RISE, which quantizes hand states to simplify hand motion prediction while preserving essential patterns, and applies a continuous relaxation that allows arm actions to diffuse jointly with these compact hand states. This design enables the policy to learn arm-hand coordination from data while preventing hand actions from overwhelming the action space. Experiments show that DQ-RISE achieves more balanced and efficient learning, paving the way toward structured and generalizable dexterous manipulation. |
|

|
Hongjie Fang*, Chenxi Wang*, Yiming Wang*, Jingjing Chen*, Shangning Xia, Jun Lv, Zihao He, Xiyan Yi, Yunhan Guo, Xinyu Zhan, Lixin Yang, Weiming Wang, Cewu Lu†, Hao-Shu Fang† CoRL, 2025 paper / data collection code / policy code / project page Develop AirExo-2, an updated low-cost exoskeleton system for large-scale in-the-wild demonstration collection. By transforming the collected in-the-wild demonstrations into pseudo-robot demonstrations, our system addresses key challenges in utilizing in-the-wild demonstrations for downstream imitation learning in the real world. Propose RISE-2, a generalizable imitation policy that integrates 2D and 3D perceptions, outperforming previous imitation learning policies in both in-domain and out-of-domain tasks, even with limited demonstrations. By leveraging in-the-wild demonstrations collected and transformed by the AirExo-2 system, without the need for additional robot demonstrations, RISE-2 achieves comparable or superior performance to policies trained with teleoperated data, highlighting the potential of AirExo-2 for scalable and generalizable imitation learning. |

|
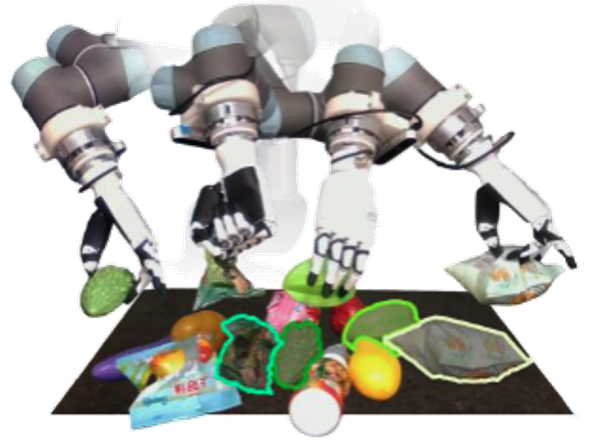
Hao-Shu Fang†, Hengxu Yan, Zhenyu Tang, Hongjie Fang, Chenxi Wang, Cewu Lu† arXiv, 2025 paper / project page Introduce AnyDexGrasp, an efficient approach for learning dexterous grasping with minimal data, advancing robotic manipulation capabilities across different robotic hands. Our results show a grasp success rate of 75-95% across three different robotic hands in real-world cluttered environments with over 150 novel objects, improving to 80-98% with increased training objects. |
|
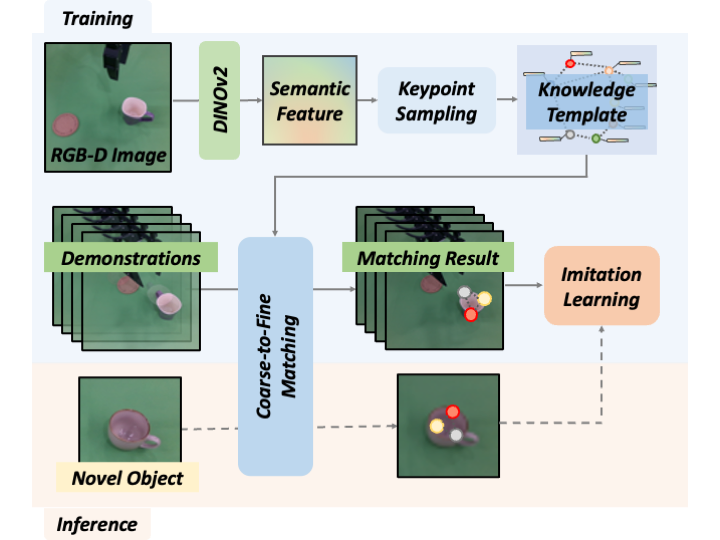
Zhuochen Miao*, Jun Lv*, Hongjie Fang, Yang Jin, Cewu Lu† IROS, 2025 paper / code / project page We propose knowledge-driven imitation learning, a framework that leverages external structural semantic knowledge to abstract object representations within the same category during imitation learning. We introduce a novel semantic keypoint graph as a knowledge template and develop a coarse-to-fine template-matching algorithm that optimizes both structural consistency and semantic similarity. |
|
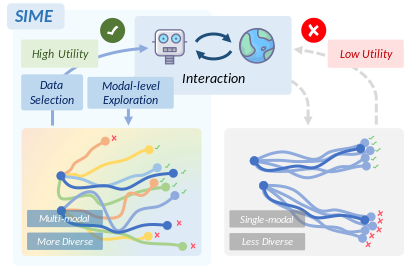
Yang Jin*, Jun Lv*, Wenye Yu, Hongjie Fang, Yong-Lu Li, Cewu Lu† IROS, 2025 paper / code / project page We found that with modal-level exploration, the robot can generate more diverse and multi-modal interaction data. By learning from the most valuable trials and high-quality segments from these interactions, the robot can effectively refine its capabilities through self-improvement. |
|
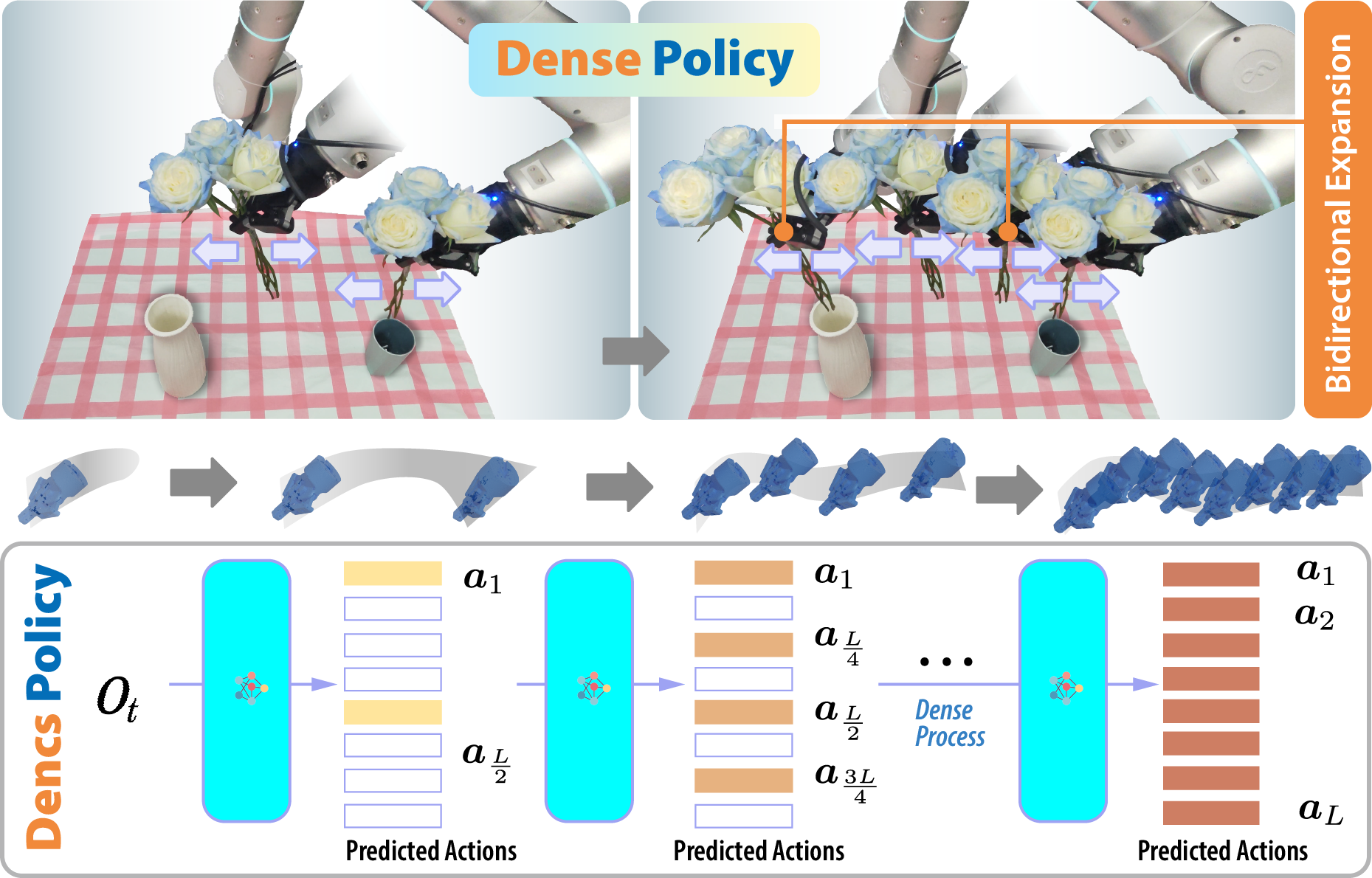
Yue Su*, Xinyu Zhan*, Hongjie Fang, Han Xue, Hao-Shu Fang, Yong-Lu Li, Cewu Lu, Lixin Yang† ICCV, 2025 paper / code / project page Propose a bidirectionally expanded learning approach that enhances auto-regressive policies for robotic manipulation. It employs a lightweight encoder-only architecture to iteratively unfold the action sequence from an initial single frame into the target sequence in a coarse-to-fine manner with logarithmic-time inference. |

|
Zihao He*, Hongjie Fang*, Jingjing Chen, Hao-Shu Fang†, Cewu Lu† RA-L, 2025 IROS, 2025 paper / code / project page / X Propose FoAR, a force-aware reactive policy that combines high-frequency force/torque sensing with visual inputs to enhance the performance in contact-rich manipulation. Built upon the RISE policy, FoAR incorporates a multimodal feature fusion mechanism guided by a future contact predictor, enabling dynamic adjustment of force/torque data usage between non-contact and contact phases. Its reactive control strategy also allows FoAR to accomplish contact-rich tasks accurately through simple position control. |

|
Yue Su*, Xinyu Zhan*, Hongjie Fang, Yong-Lu Li, Cewu Lu, Lixin Yang† RA-L, 2025 paper / code / project page Propose MBA, a novel module that employs two cascaded diffusion processes for object motion generation and robot action generation under object motion guidance. Designed as a plug-and-play component, MBA can be flexibly integrated into existing robotic manipulation policies with diffusion action heads. Extensive experiments in both simulated and real-world environments demonstrate that our approach substantially improves the performance of existing policies across a wide range of manipulation tasks. |
|
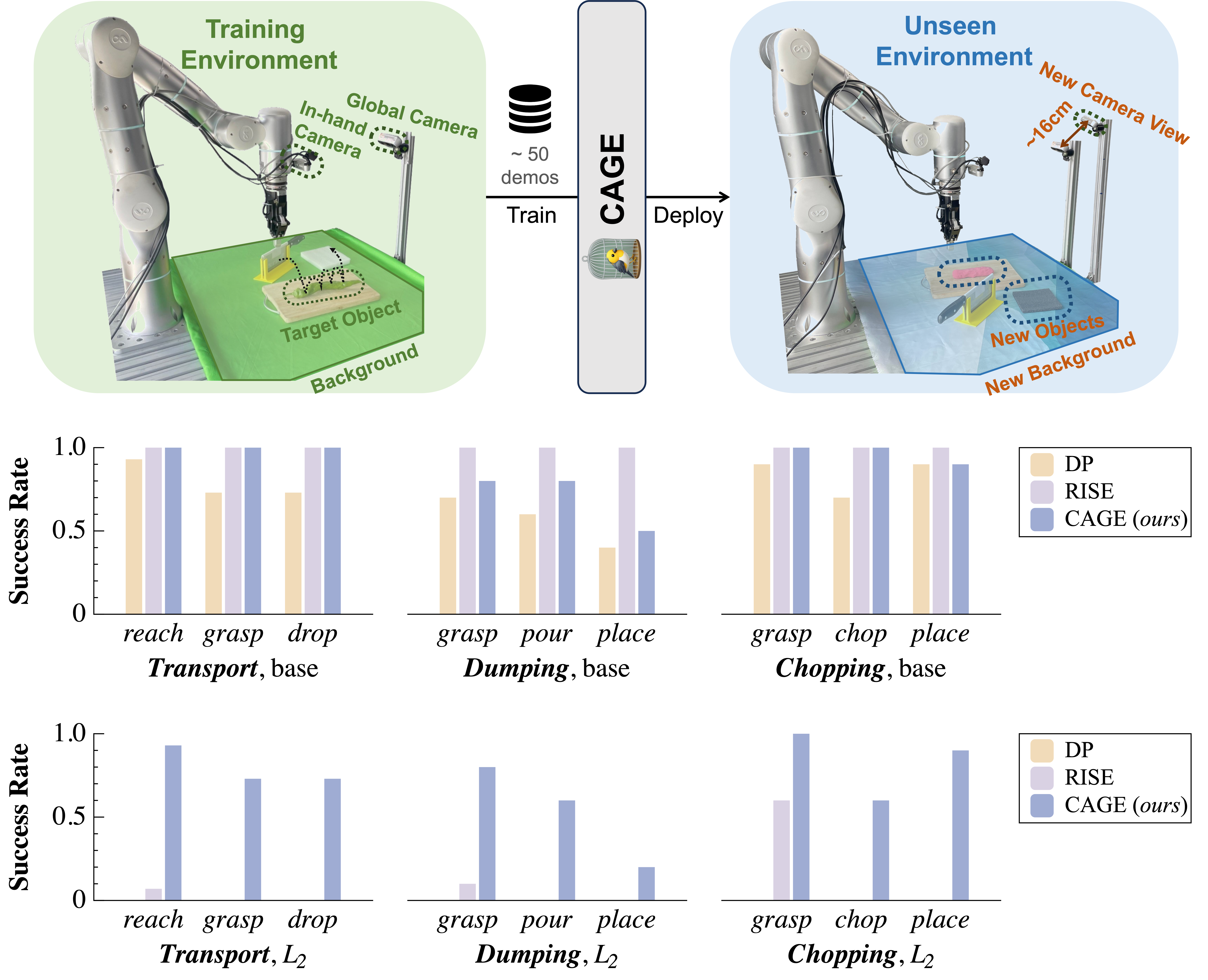
Shangning Xia, Hongjie Fang, Cewu Lu†, Hao-Shu Fang† ICRA, 2025 paper / code / project page Introduce CAGE, a data-efficient generalizable robotic manipulation policy. With less than 50 demonstrations in the mono-distributed training environment, CAGE can effectively generalize to similar and unseen environments with different levels of distribution shifts (background, object and camera view changes), outperforming previous state-of-the-art policies. This work makes a step forward in developing data-efficient, scalable, and generalizable robotic manipulation policies. |
|
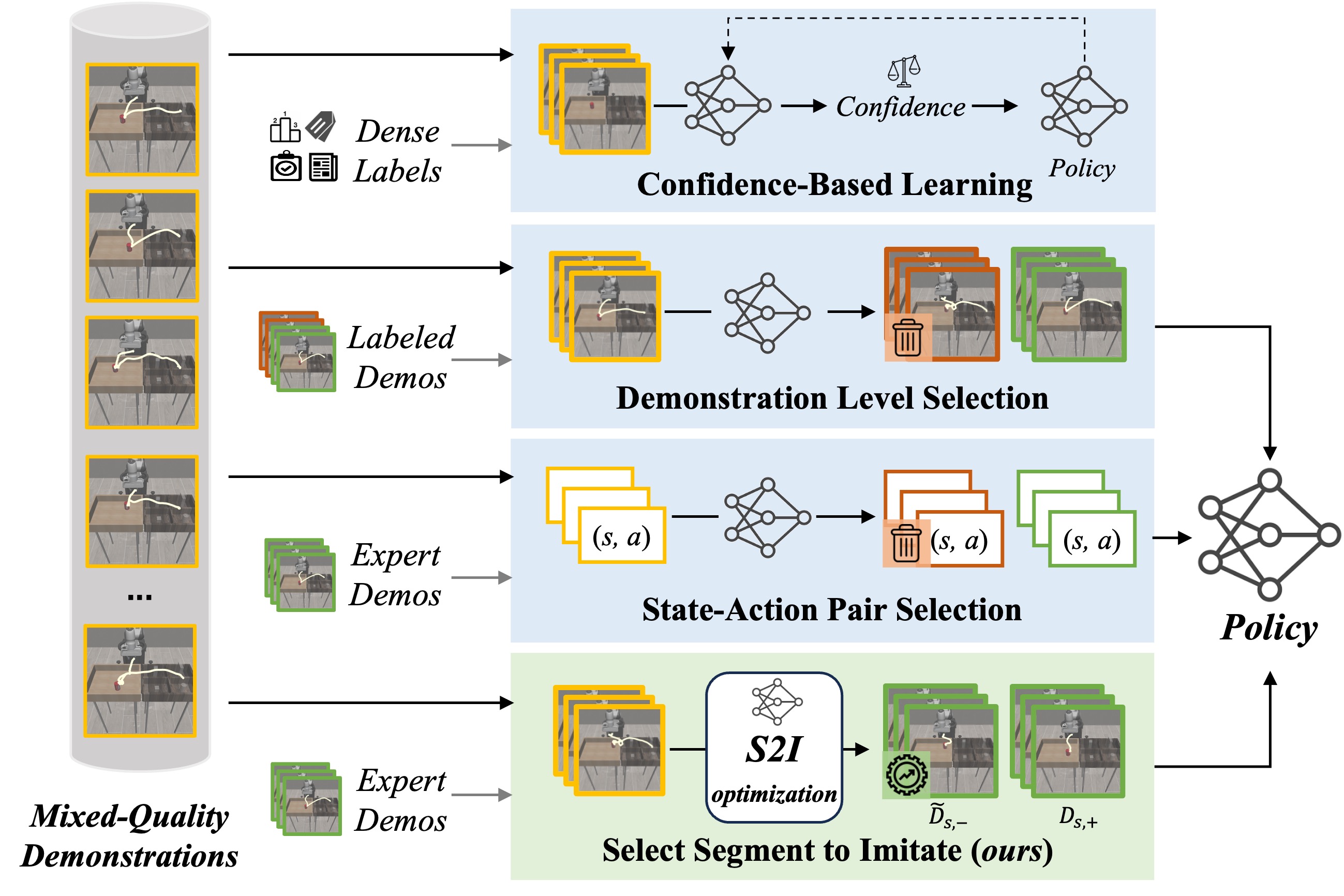
Jingjing Chen, Hongjie Fang, Hao-Shu Fang, Cewu Lu† ICRA, 2025 paper / code / project page Introduce S2I, a framework that selects and optimizes mixed-quality demonstration data at the segment level, while ensuring plug-and-play compatibility with existing robotic manipulation policies. With only 3 expert demonstrations for reference, S2I can improve the performance of various downstream policies when trained with mixed-quality demonstrations. |
|
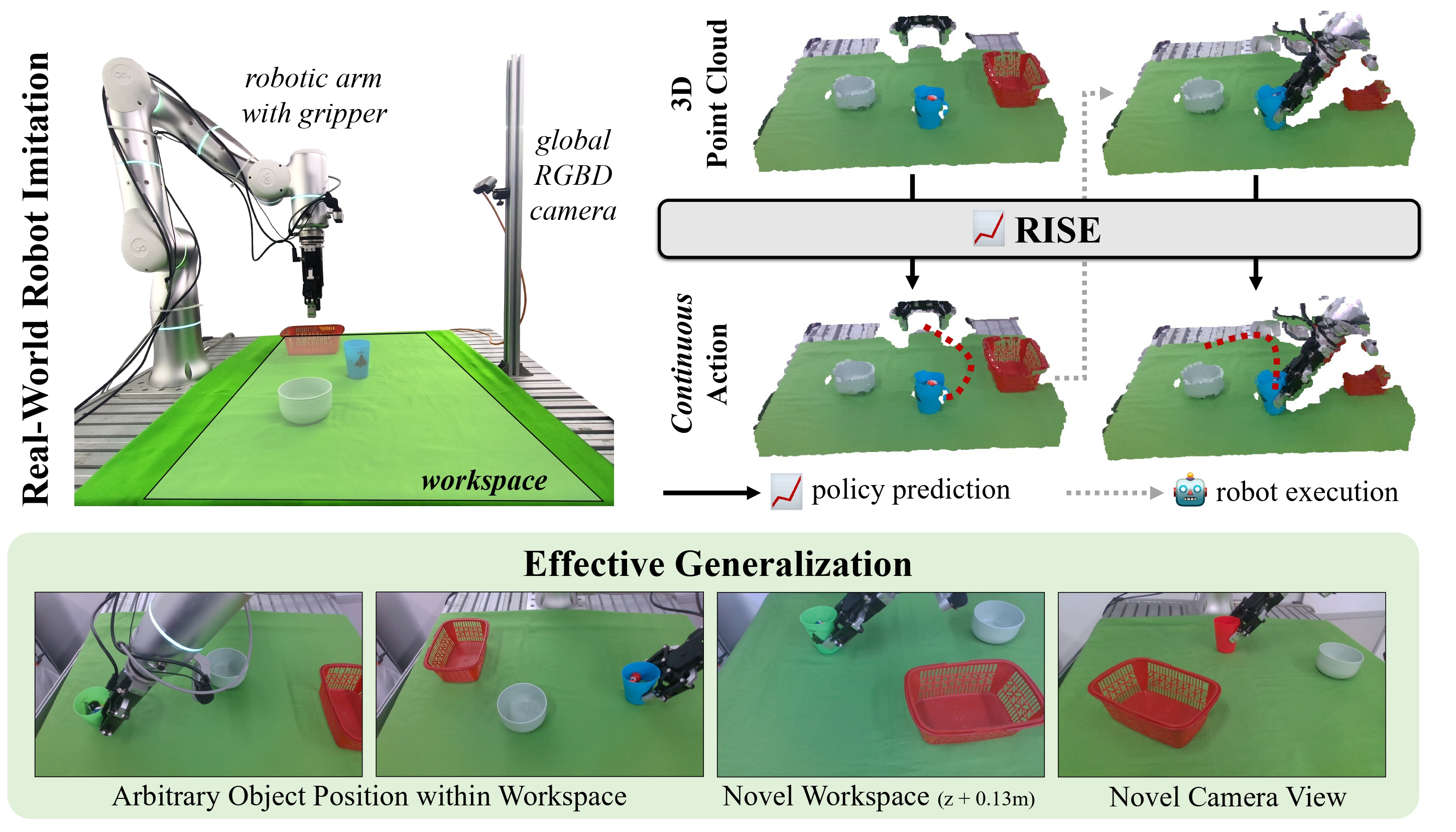
Chenxi Wang, Hongjie Fang, Hao-Shu Fang†, Cewu Lu† IROS, 2024 paper / code / project page / X Propose RISE, an end-to-end baseline for real-world robot imitation learning, which predicts continuous actions directly from single-view point clouds. Trained with 50 demonstrations for each real-world task, RISE surpasses currently representative 2D and 3D policies by a large margin, showcasing significant advantages in both accuracy and efficiency. |

|
Open X-Embodiment Collaboration, [...], Hongjie Fang, [...] (194 authors) ICRA, 2024 paper / project page / dataset Introduce the Open X-Embodiment Dataset, the largest robot learning dataset to date with 1M+ real robot trajectories, spanning 22 robot embodiments. Train large, transformer-based policies on the dataset (RT-1-X, RT-2-X) and show that co-training with our diverse dataset substantially improves performance. |

|
Hongjie Fang*, Hao-Shu Fang*, Yiming Wang*, Jieji Ren, Jingjing Chen, Ruo Zhang, Weiming Wang, Cewu Lu† ICRA, 2024 paper / project page / X Develop AirExo, a low-cost, adaptable, and portable dual-arm exoskeleton, for joint-level teleoperation and demonstration collection. Further leverage AirExo for learning with cheap demonstrations in the wild to improve sample efficiency and robustness of the policy. |
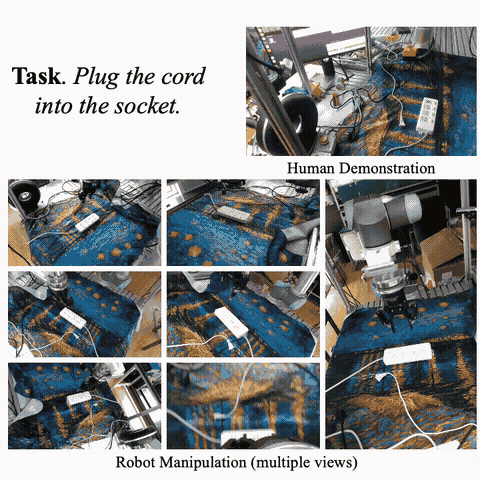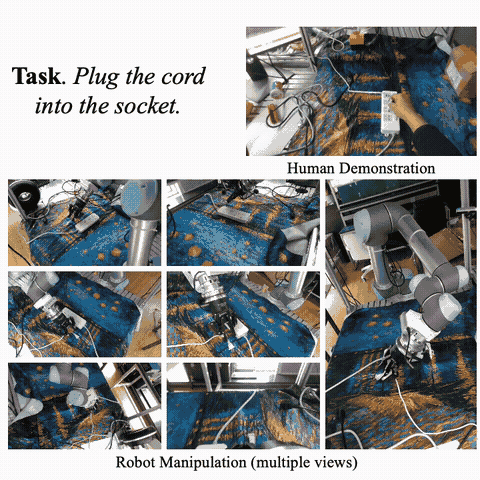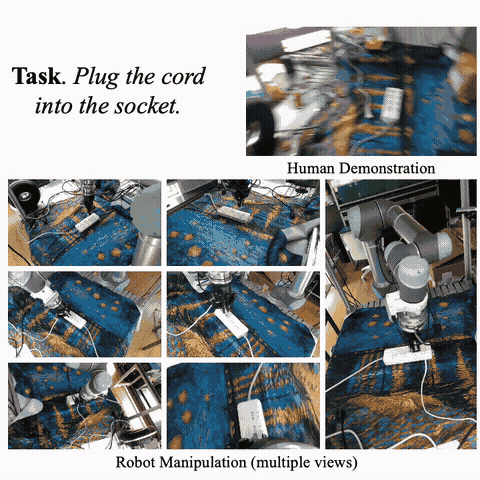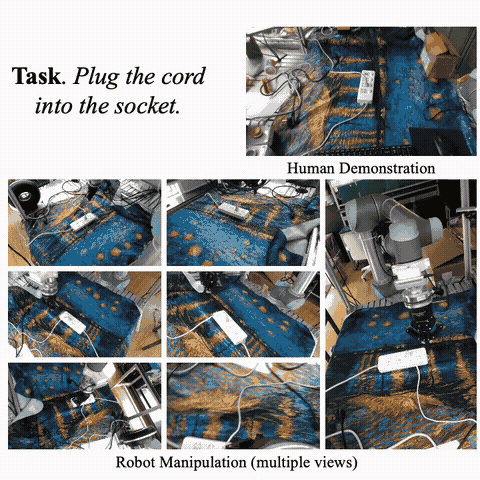
|
Hao-Shu Fang, Hongjie Fang, Zhenyu Tang, Jirong Liu, Chenxi Wang, Junbo Wang, Haoyi Zhu, Cewu Lu† ICRA, 2024 paper / API / project page / X Collect a dataset comprising over 110k contact-rich robot manipulation sequences across diverse skills, contexts, robots, and camera viewpoints, all collected in the real world. Each sequence in the dataset includes visual, force, audio, and action information, along with a corresponding human demonstration video. Put significant efforts in calibrating all the sensors and ensures a high-quality dataset. |

|
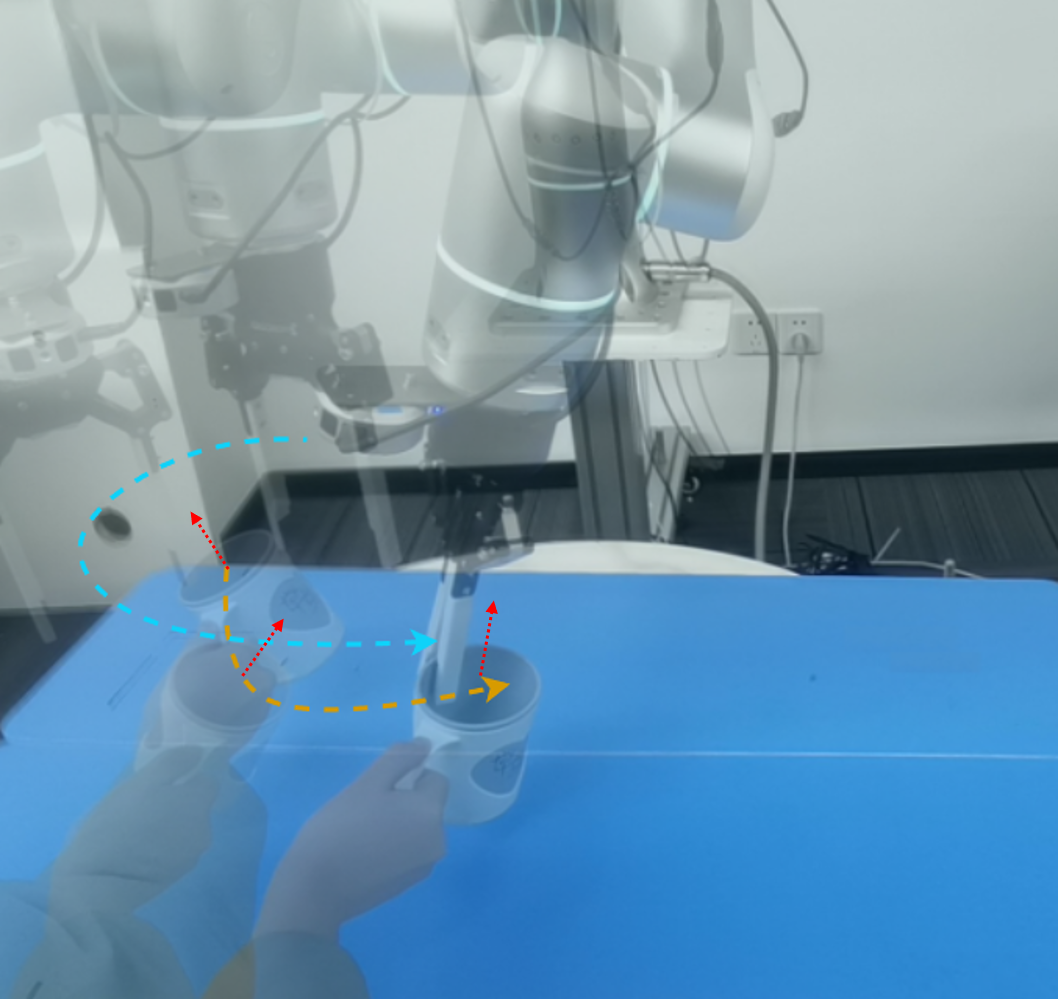
Gu Zhang, Hao-Shu Fang, Hongjie Fang, Cewu Lu† IROS, 2023 paper Propose an approach for effective and robust flexible handover, which enables the robot to grasp moving objects with flexible motion trajectories with a high success rate. The key innovation of our approach is the generation of real-time robust grasp trajectories. Designs a future grasp prediction algorithm to enhance the system's adaptability to dynamic handover scenes. |
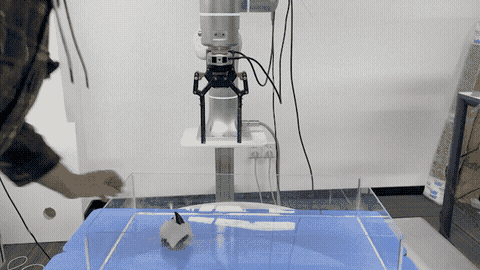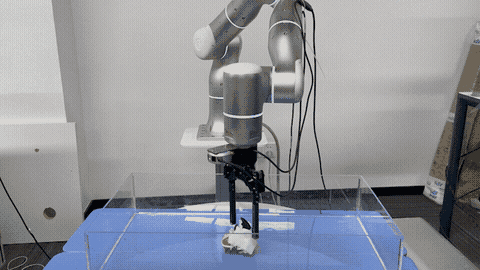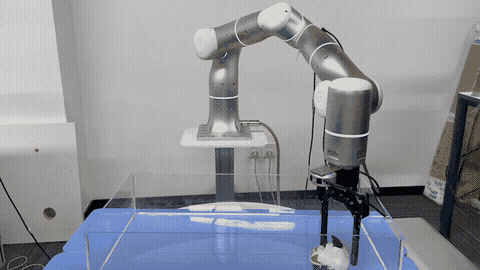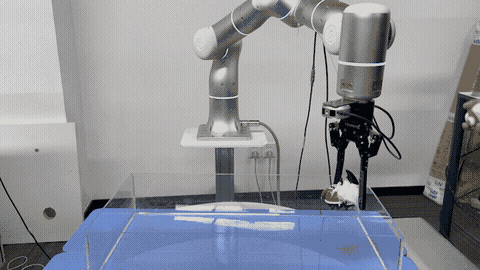
|
Jirong Liu, Ruo Zhang, Hao-Shu Fang, Minghao Gou, Hongjie Fang, Chenxi Wang, Sheng Xu, Hengxu Yan, Cewu Lu† CVPR, 2023 paper / project page Focus on semantic consistency instead of temporal smoothness of the predicted grasp poses during reactive grasping. Solve the reactive grasping problem in a target-referenced setting by tracking through generated grasp spaces. |

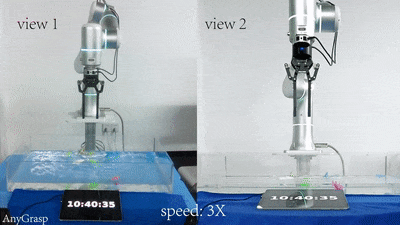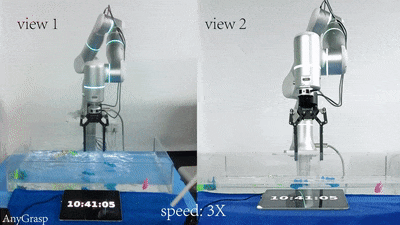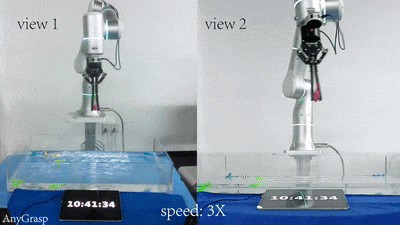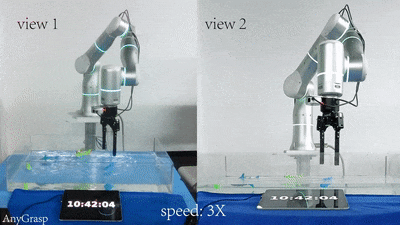
|
Hao-Shu Fang, Chenxi Wang, Hongjie Fang, Minghao Gou, Jirong Liu, Hengxu Yan, Wenhai Liu, Yichen Xie, Cewu Lu† T-RO, 2023 ICRA, 2024 paper / SDK / project page Propose a powerful AnyGrasp model for general grasping, including static scenes and dynamic scenes. AnyGrasp can generate accurate, full-DoF, dense and temporally-smooth grasp poses efficiently, and it works robustly against large depth sensing noise. |

|
Hongjie Fang, Hao-Shu Fang, Sheng Xu, Cewu Lu† RA-L, 2022 ICRA, 2023 paper / code / project page Propose TransCG, a large-scale real-world dataset for transparent object depth completion, along with a depth completion method DFNet based on the TransCG dataset. |
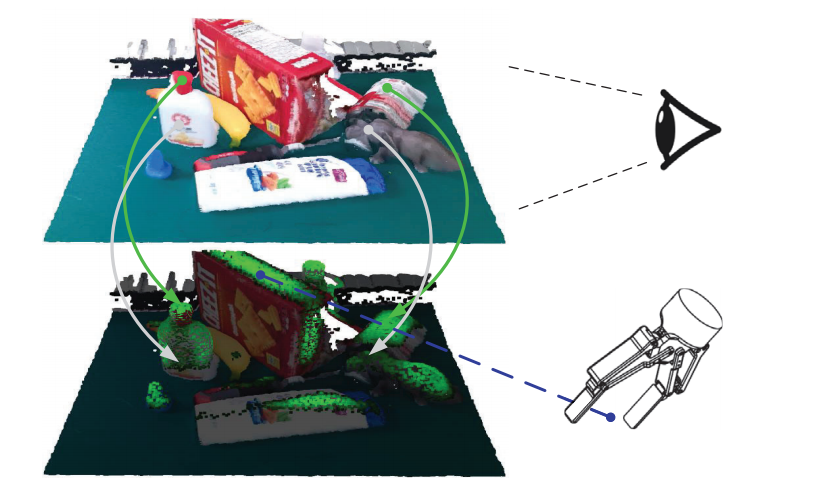
|
Chenxi Wang, Hao-Shu Fang, Minghao Gou, Hongjie Fang, Jin Gao, Cewu Lu† ICCV, 2021 paper Propose graspness, a quality based on geometry cues that distinguishes graspable area in cluttered scenes, which can be measured by a look-ahead searching method. Propose a graspness model to approximate the graspness value for quickly detect grasps in practice. |
|
|

|
Hongjie Fang research project, code Provides an easy and unified interface for robots, grippers, sensors and pedals. |
|
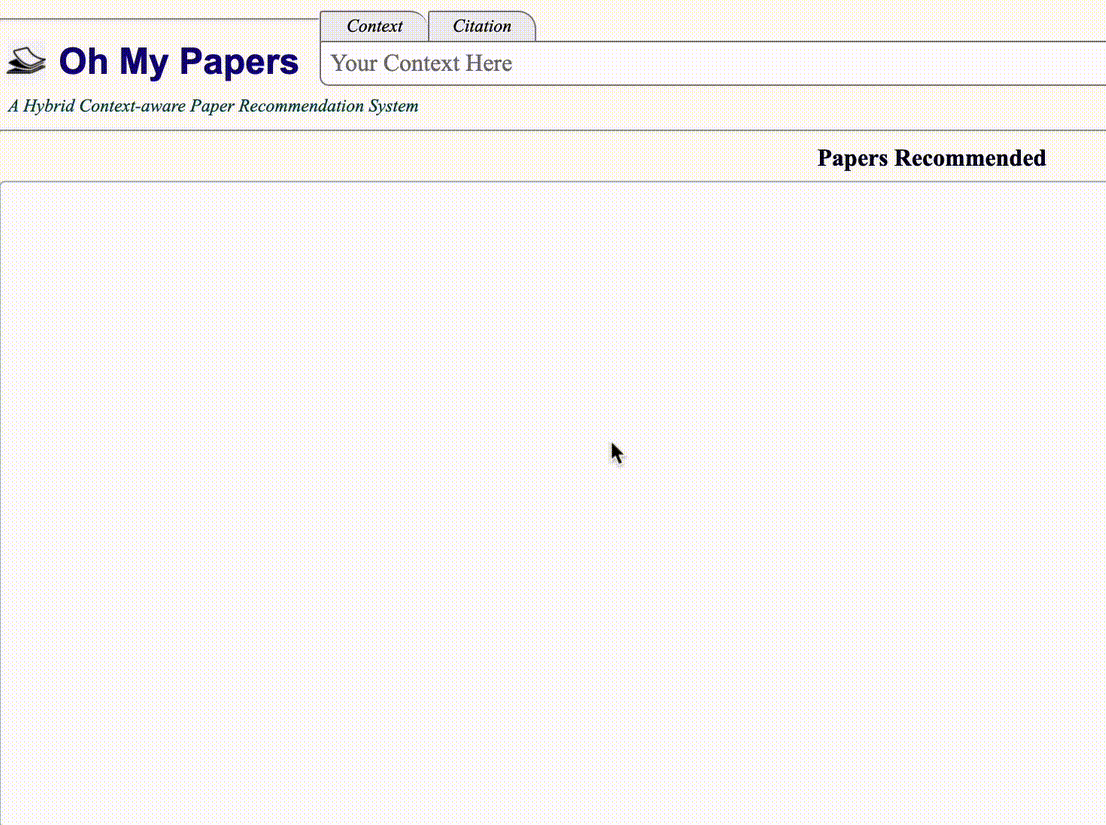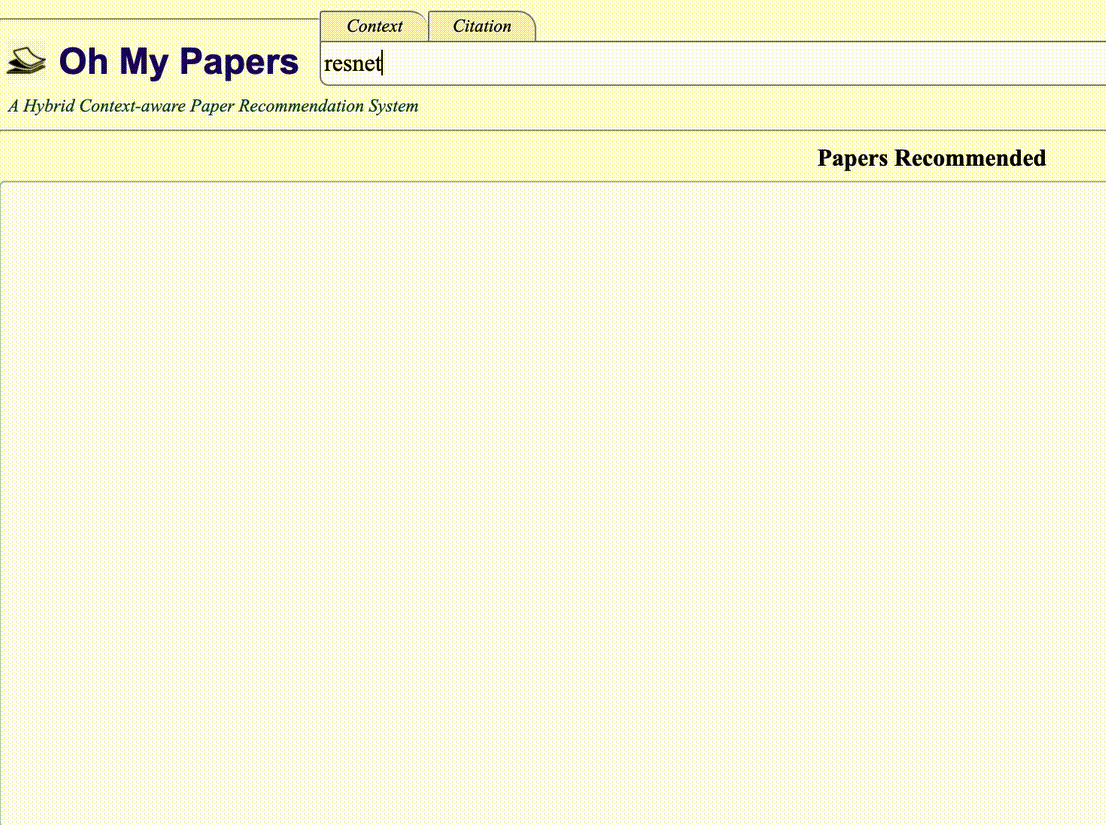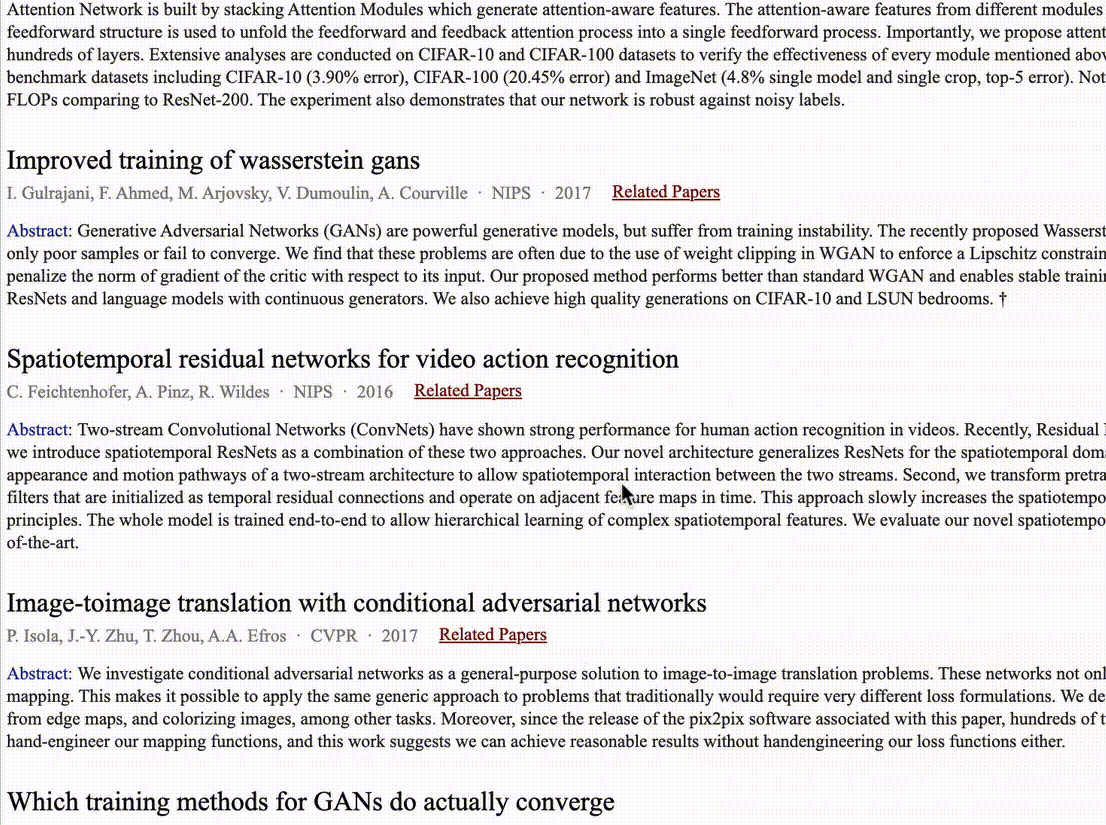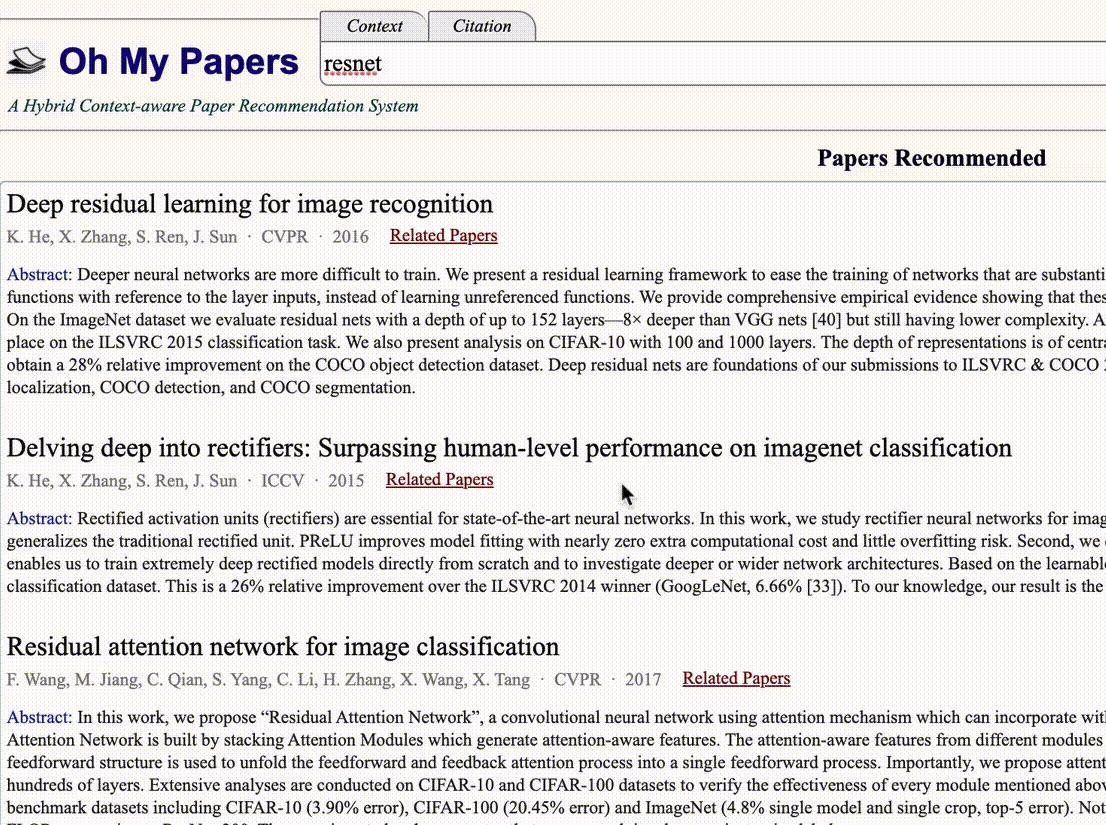
Hongjie Fang, Zhanda Zhu, Haoran Zhao course project of SJTU undergraduate course "Mobile Internet" code / demo / report Proposes that we can learn "jargons" like "ResNet" and "YOLO" from academic paper citation information, and such citation information can be regarded as the searching results of the corresponding "jargon". For example, when searching "ResNet", the engine should return the "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition", instead of the papers that contains word "ResNet" in their titles, as current scholar search engines commonly return. |
|
Reviewer for Conferences: ICRA (2023-2026), IROS (2023-2025), CoRL (2025), ICLR (2025), NeurIPS (2025), CVPR (2026). |
|
|
|
I collaborate closely with Hao-Shu Fang @ MIT, Chenxi Wang @ Noematrix, Shangning Xia @ Noematrix, Lixin Yang @ SJTU, Jun Lv @ Noematrix and Shiquan Wang @ Flexiv. I welcome opportunities for discussions and potential collaborations, and I am particularly interested in working with highly motivated undergraduate and master's students. Please feel free to contact me via email. I'm fortunate to work with the following students:
|
|
I share some of my notes in the courses I took at graduate school in this page. More notes during my undergraduate study can be found in this repository. |
|
The website is built upon this template. |